Logistics Strategy Definition:
What is a logistics strategy? Logistics strategy is the set of guiding principles, driving forces and ingrained attitudes that assist to coordinate goals, plans and policies, and which are reinforced through conscious and subconscious behaviour within and between partners across a network.
When it comes to company strategy, logistics was formerly thought of as nothing more than managing the transport network and warehouses. Companies now recognize that logistics planning is essential to corporate strategy, particularly in light of the pressing requirement for sustainability to be included into business operations.
Because carbon emissions have an impact on climate change, logistics can be crucial in reducing a company’s environmental impact.
In addition, we are in the midst of a period of profound global transformation that is changing the socio-economic and political environments. Supply and value chains are coming under more and more pressure, thus they could need constant assessment and revision.
Importance of Logistics planning and strategy : It will assist in streamlining service levels to the point where a business is operating at its most economical and energy-efficient levels.
Logistics Strategy vs Logistics Operations
The supply chain management (SCM) process encompasses both logistics strategy and logistics operations.
Logistics strategy makes use of management principles to ensure that workflow is optimized. It entails warehousing, commodities flow, services, and information efficiency design, implementation, and maintenance.
The manufacturing process is usually the only focus of logistics operations. Operations may be referred to as planning in the service industry, but management of that part of the organization is carried out in a similar manner. Simply said, it is concerned with the movement (flow and storage) of items, information, products, and services within the supply chain, whereas logistics operations are concerned with manufacturing, materials handling, and inventory management.
Within the logistics and operations management of the organization, logistics strategy and logistics operations work in tandem. All of this should be evaluated in terms of whether the end user’s needs for pricing, quality, and availability have been met effectively. Importance of Logistics strategies rely n Customer satisfaction.
Customer satisfaction is a top goal in decision-making because the end user determines whether or not a retailer’s customer base will survive.
There are four options to consider:
• Adapt Strategy
Adapt strategy is not something that is done in a formal way. A common attitude is that “our approach is not to have a strategy.” Operating decisions are made in response to current needs, with financial goals serving as the primary guiding principle.
• Traditional
Financial goals are the key guiding element once again, but this time they are attained through a structured planning procedure. Because it is the oldest and most influential alternative, it is referred to as “classical.”
• Be accommodating.
Decisions are now again being made on a daily basis, but financial goals are no longer the major issue.
• The problem is systemic.
Assumes that there is no contradiction between the ends and means of achieving corporate objectives.
Six Concepts for Logistics Strategy Formulation
• Total Cost Concept – Tradeoff conflicting costs at optimum
• Differentiated distribution – Not all products should be provided the same level of customer service
• Mixed strategy – A pure strategy has higher costs than a mixed strategy
• Postponement – Delay formation of the final product as long as possible
• Shipment consolidation – Smaller shipment sizes have disproportionately higher transportation costs than larger ones
• Product standardization – Avoid product variety since it adds to inventory
Considerations: The Logistics planning triangle.
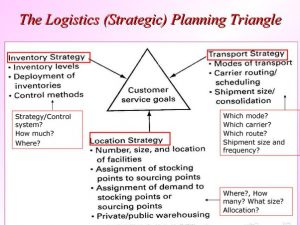
The logistics strategic planning triangle, also known as the supply chain triangle, is a concept that captures the idea that organizations deliver different types of services, which come at a certain cost and require a certain amount of inventory, or more generically, cash. The three corners of the triangle represent service, cost, and cash.
1. **Service**: This refers to the level of service provided to customers. High service levels often lead to increased sales but can also result in higher costs.
2. **Cost**: This includes all costs associated with producing and delivering products or services. Reducing costs can improve profitability but may also impact service levels.
3. **Cash**: This represents the amount of capital tied up in inventory. Reducing inventory can free up cash but may also affect service levels.
Balancing these three elements might be the essence of supply chain management. However, decisions in one corner of the triangle impact the others, creating tension. For example, sales and marketing managers typically focus on service, while production and supply chain managers focus on cost.
Balancing these competing goals is a challenging task that often falls to supply chain managers.
The goal is to maximize shareholder value via sustainable growth, which means aligning the three corners of the supply chain triangle. To achieve this balance, companies need explicit strategy and data-driven transparency. They must prioritize their focus areas instead of trying to excel in all three areas simultaneously.
In summary, the logistics strategic planning triangle provides a framework for understanding and managing the interdependencies between service, cost, and cash in supply chain management. It emphasizes the need for strategic planning and decision-making to balance these competing objectives and maximize overall business performance.
Subscribe to our channel & watch part 1 and 2 on Logistics strategy.
Example : DHL Case DHL STRATEGY 2025
Logistics Strategy Lecture video | Part 1

Logistics Strategy Lecture video | Part 2

{“title”:”Share & Follow”}
